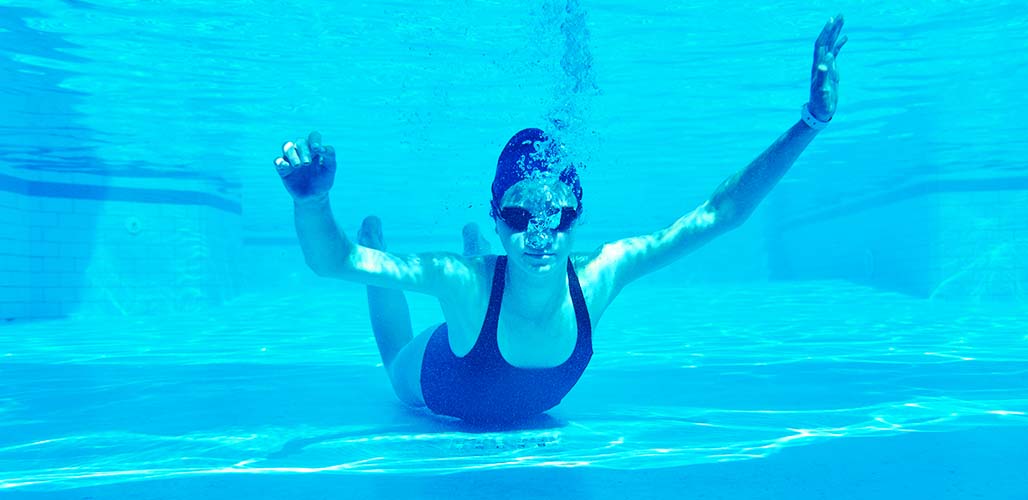Can Some People Not Float?
Can some people not float? Have you ever been in the pool and tried to float on your back, but simply couldn’t? No matter how much your swimming instructor told you to relax your muscles and spread your back evenly, you still can’t do it, so what gives? Scientifically speaking, some people cannot, in fact, float. This is mainly due to their body composition and muscle-to-fat ratio. You can train yourself to float more easily and some bodies of water are easier to swim in than others, but it’s a sad fact that it might be hopeless if you’re built like a superhero. Today, I’ll take a closer look at why you might not be able to float, and tips to make it easier!
Contents
- Can some people not float – my experiences
- Why can some people not float?
- Why do I float in the sea but not in the pool?
- How do I float?
Can Some People Not Float? My Experience
When I was a child, I used to take swimming lessons but I wasn’t very good at it. I was a chubby kid who didn’t have the best lungs, and I was always too tense so I’d struggle to stay up on the water. Years later, as a teenager, I had hit the gym, lost weight, and I was proud of myself for gaining muscle.
I was on vacation, though, and I hadn’t swum in a very long time. I was with my sister, who had no idea how to swim, but she was floating on her back. She kept telling me to do it but every time I tried, I simply couldn’t. I did everything she did, but alas, nothing worked, and I stuck to diving underwater. What I didn’t know was that the gym played a part in this.
Why Can Some People Not Float?
Before we dive into anything we need to define a very important term: Buoyancy. This is something’s ability to float in water or any other fluid. Another important term to remember is density. Okay, that’s terrific, but what does that have to do with floating? Well, if you take a trip down memory lane to science class, you will remember that the more buoyant an object is and the lesser density it has, the easier it is to float in water!
The thing is, muscle tissue is denser than fat. So, simply, if you have more fat, you float easier, but if you have more muscle, you don’t float so easily. Of course, in some cases, you may not be using the right techniques to float. But, even with the right method, very muscular people can struggle to stay afloat in the water.
Does this mean you can’t swim, though? Not exactly. Floating while swimming and floating while resting are different. When swimming, other parts of your body are helping you out, so you push yourself to the surface of the water using your legs and arms. While resting, however, you’re relying entirely on how buoyant you are so it’s difficult.
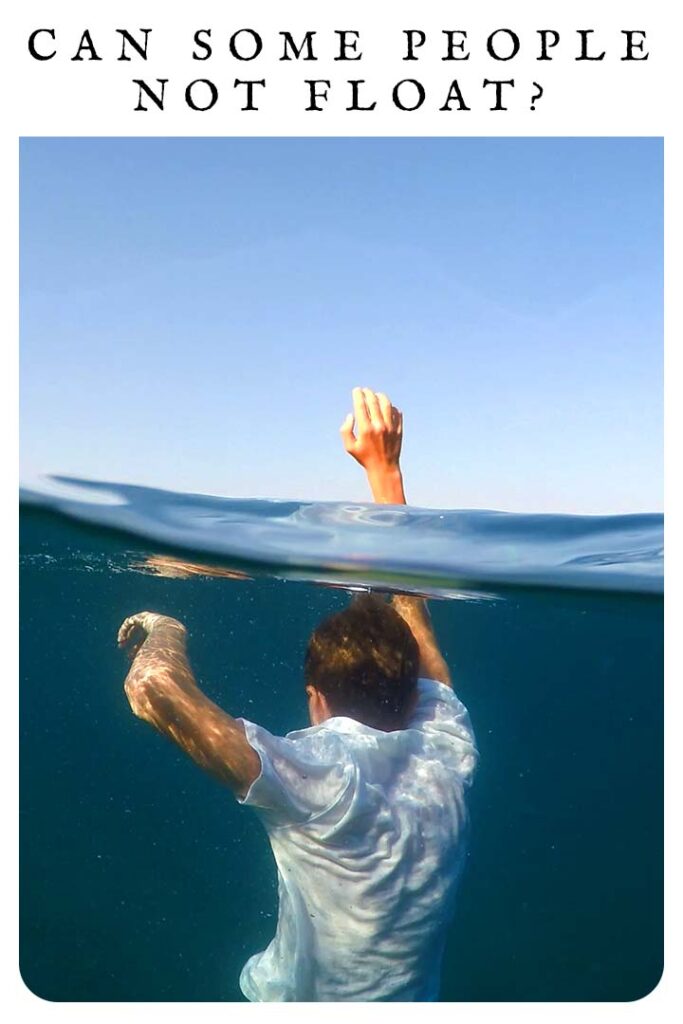

Why Do I Float in the Sea or Ocean But Not in the Pool?
Some more science facts for you: Adding salt to water increases its density. So, it’s more likely to support an object even if it’s not very buoyant. A simple experiment by Scientific American was conducted using an egg, salt, and a measuring cup. The salt added to the water was able to hold the egg up. This is the same for people. Amazingly, in seawater, salt makes up around 3.5% of the water’s weight. That’s A LOT of salt, which is capable of holding less buoyant people up when they try to float.
So, if you can’t float in the pool, try giving the sea or ocean a try. Most famously, the Dead Sea has the highest percentage of salt compared to other water bodies, so it’s very easy for a lot of people to float there.
How Do I Float?
Don’t give up so easily on floating, though. There are several techniques you can try to incorporate that would help you float. My first piece of advice is to just calm down and try to spend time either underwater or close to the surface in a calm state without gasping for air. Spending time being calm in the water lets your body get to know the water better and exploit the water’s natural support.
My second tip is to try to float upright. Research in The International Journal of Aquatic Research and Education tackled the idea of floating vertically first.Number three is all about spreading your body weight. As we have discussed, the more compact and the less space you take up, the harder it will be to float. So, spread your legs and arms as wide as possible, and don’t be too embarrassed by the water; everyone is doing it.
A neat trick that I myself learned during swimming practice that helped me immensely was to take a deep breath and hold it in when trying to float either vertically or horizontally. This treats your body like a balloon and helps you become less dense, so the water can lift you up. Get your diaphragm moving, hold your breath, spread wide, and just relax.
Can Some People Not Float? A Summary
Floating might seem like a pretty basic skill, but it’s not as easy for everyone to learn. The more muscle mass you have, the harder it can be to float. But, the tips I laid out above can be a great starting point, even if you do have plenty of muscle making things harder!
More Swimming Questions Answered
- Does swimming make you smarter?
- How can I get better at cold water swimming?
- Are swimmers fitter than cyclists?
- What muscles does backstroke use?
- Will a wetsuit help me float?
References
- Rushall, B. ‘Floatation in Swimming: The Forgotten Technique Modifier’, Swimming Science Bulletin (2007)
- ‘Why is the Ocean Salty?’, U.S. Geological Survey
- ‘Salty Science: Floating Eggs in Water’, Scientific American
- Andrews, A. ‘How to Help People Float’, International Journal of Aquatic Research and Education (2019)